By Panos Blatsoukas on 23 Sep 2019

Alright folks, another memorable BrightonSEO went down in the SEO history books last week, and once again it was savage. As part of our ongoing training and team-building initiative here at Wolfgang Digital, the majority of the SEO crew headed over to Brighton to spend some quality time together and attend the world’s greatest SEO conference!
We had the chance to attend lots of interesting talks and get bags of actionable SEO insights from some of the world's industry leaders.
Every year this quaint seaside town becomes a hotbed for our industry's movers and shakers and it’s in the bars and cafes that hot topics and trends are discussed. During our trip we met old friends and made a bunch of new ones to share our nerdy SEO jokes with. As always there was an amazing lineup of speakers, and today we're going to share with you our key takeaways that we brought back to the Emerald Isle.
Greg Gifford - Beetlejuice's Guide - Entities and the Future of SEO
What is an entity I hear you ask?
An Entity is ‘a thing with distinct and independent existence’ according to online Dictionary Lexico. But in the SEO world an entity is far more than that. Entities can exist out of language. An entity can be from a person, an object or a brand, to a colour, a date or even an idea. For Google, an entity is ‘a thing or concept that is singular, unique, well defined and distinguishable’.
That said, we completely agree with Greg that entities are one of the most important concepts in modern SEO and we should be focusing our actions based on that, rather than trying to optimise individual page elements. Already, for a few years at Wolfgang, we’ve been embracing a ‘let’s own this featured snippet’ mindset and never publish anything without being confident to read it out loud or send it to a friend!
Local SEO is also becoming a key component to success as Google My Business is a direct interface to Google’s entity base about any online business.
Key Takeaways
- Entities are becoming the most critical concept in SEO and they should be our focus on every task going forward.
- Google My Business (GMB) is a great place to build up an entity. Using the features available such as: Reviews, Directions, Google posts, Photos and the Q&A section which all join together to build an entity.
- As progressive SEO’s we should be matching our content to provide the best answer to the users search intent all the while focusing our answers in a unique way.
- Real-world signals and offline actions related to business entities are going to play a major role in rankings as the machines become more intelligent.
Tim Soulo - Rethinking The Fundamentals of Keyword Research With Insights From Big Data
Tim Soulo from Ahrefs talked about an old-time SEO essential topic, Keyword Research, and gave some solid pieces of actionable insights that we can all use and improve upon. Keyword Research is one of the most important skills any SEO can develop, it’s always evolving and there are many ways that it can be done.
Tim introduced BrightonSEO to his own three-step approach:
1. Total search traffic potential
Pages will never rank for only one or even a handful of keywords. In fact, Tim and his team at Ahrefs conducted a study and found that a page ranking number 1 for a specific keyword, also ranks for approximately 1,000 additional keywords.
Every keyword or topic has its own search demand curve, which includes all the keyword variations for that specific search term.
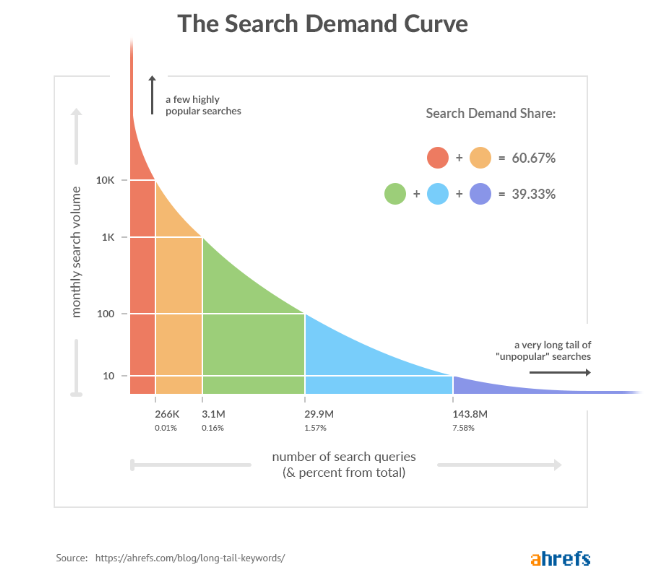
So the total search traffic potential for each topic or keyword highly depends on the various ways people are searching for it, as everyone has their own method to search and find something on the internet.
You should make sure to analyse all the top-ranking pages of the keywords you want to rank for, get the total search traffic potential and focus more on long-tail keywords.
2. Business potential
This is a great one. You might be ranking number one for a keyword with loads of search volume. You might get a considerable amount of traffic from that keyword as well. However, is that enough? As Tim pointed out, you should be making sure that the traffic you get, is also converting.
To do this, you can apply a business potential score for each page of the website. This will help you focus on pages that drive people to the website but also result in some juicy conversions. We even share Tim’s business potential score below:
3 - your product is an almost irreplaceable solution to the problem
2 - your product is helpful for the problem but can be solved without it
1 - your product is barely relevant to the problem
3. Ranking Potential
Most SEOs aim to rank number one on Google for as many pages and as many queries as possible. However, Tim explained that ranking number 1 is overrated nowadays and it doesn’t guarantee the most visitors and traffic to your website. In fact, a study from Ahrefs based on 100K search queries found that the top-ranking page gets the most total search traffic only 49% of the time.
So how do we outperform #1? Focusing on search intent is a key element of success.
Key Takeaways:
- Search intent is what we should be focusing on when conducting any Keyword Research.
- Always look for the total search potential for a topic as it has its own search demand curve.
- Don’t rely on search volume for keywords. Make sure to analyse the top-ranking pages to understand how many keywords those pages are ranking for and what is the true potential for your pages.
Jan-Willem Bobbink - What I learned about SEO from building websites with the 10 most used JS frameworks
Jan Willem talked about how JavaScript and Single Page Applications are dominating the internet and how this evolved over the last couple of years. Jan used the 10 most popular JavaScript frameworks and the results were mindblowing!
Why JavaScript is challenging?
Many are unaware that Googlebot is not a real user and always starts with a blank browser and history. It can’t use cookies, session data or local storage after the first visit, all elements that could improve your website's loading times.
Jan advises and we at Wolfgang agree that developers should always avoid full client-side rendering as it can impact upon performance for both your valuable visitors and search engines. Server-side rendering is always what we’d recommend (delighted to see that we are on the same page as Mr Willem!)
Unfortunately, server-side rendering can cause skews in analytics data and even double log page views.
Thankfully, there is a selection of tools out there allowing us to test JavaScript on websites. For example, you can use the URL Inspection Tool through Google Search Console, or the View Rendered Source plug-in via Chrome 77.
Key Takeaways:
- JavaScript isn’t going anywhere as more developers are using it to build websites. In fact, more than 71% of the developers are using it. (Even though it uses massive resources and can sometimes be very detrimental to SEO)
- Always make sure to include the most important elements of the page on the initial HTML. Why? Google rendering - Google performs two waves of indexing for all the websites. In the first wave, HTML (and CSS) will be crawled and indexed almost instantly. It may take a few hours or even over a week for Google to come back to your website on the second wave to render and index any JavaScript generated data.
- Make sure to use the minimum amount of JavaScript on every page where possible in order to increase performance. This is because crawling JavaScript is very expensive. The process takes time, processor power, memory and other resources.
Jamie Alberico - Think like a Bot, Rank like a Boss: How Googlebot Renders Websites
Jamie showed the audience how Googlebot sees websites and their content and how web crawlers build their view/understanding of a webpage. She explained the two waves of indexing (as discussed above) and what we should be focusing on to overcome and prevent any indexation issues.
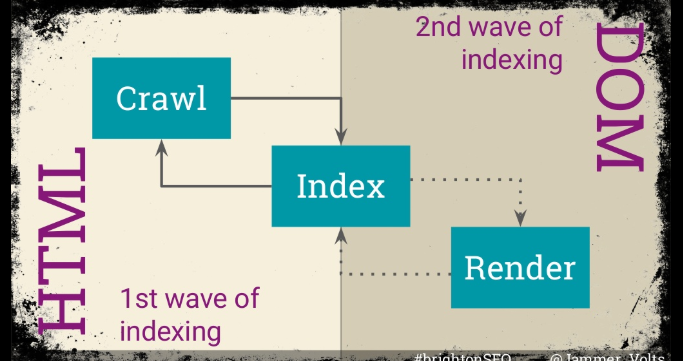
With Google driving over 95% of all traffic to the majority of our client's websites, we know we must ensure all of our content is accessible and visible through Google’s eyes to ensure these pages are indexed the way we expect them to be. Rendering can be tricky due to Google’s two-wave process of indexing. We should be aware that there is a delay between indexing HTML pages and Javascript pages and that can cause indexing issues.
What is Google’s Web Rendering Service (WRS) and how it works?
- Website URL is pulled from the crawl queue
- Googlebot requests the URL and downloads the initial HTML
- The HTML is passed to the processing stage which extracts all links
- Links go back on the crawl queue
- The page queues for rendering once the initial resources are crawled
- When sources become available, the pages are being rendered by Chromium
- The rendered HTML goes back to processing
- Finally, the rendered content is indexed
Google’s WRS doesn't retain any cookies or any data at all and doesn’t have any UI or visual elements. Googlebot wants to be polite and acts as ‘a good citizen of the web’ as it will pull back on crawling when a server is responding with errors ensuring that overloading is avoided.
Jamies’ tips to optimise high JavaScript-depended websites
- Make sure the important elements of the page are within the HTML code that Google can see almost immediately.
- Maintain content consistency across mobile and desktop.
- Make use of ‘nofollow’ across the website. ‘Nofollow’ is an attribute that instructs Google not to consider a specific link pointing to another page as a ‘vote’ to that content.
- Make sure to load the important content of a page sooner.
- Choose the rendering strategy that best suits your business.
- Perform test to detect any issues.
Key Takeaways:
- Maintain a good relationship with your developers - you’ll get better results, believe us we know!!!
- Include the content that matches the search intent in the initial HTML
- Maintain consistency across your website for both mobile and desktop results
Rory Truesdale - Mining the SERP for SEO, Content & Customer Insights
Rory helped us to go deeper into the SERPs’ language and how we can analyse it using the coding language Python to get an idea of what Google thinks searchers are actually searching.

Little known fact: Google rewrites the SERPs meta description 84% of the time, based on this study by Conductor. As SEO’s we can turn this into our advantage by scraping those results and uncover what Google is algorithmically changing. We can do that by utilising Python scripts within Jupyter, an open-source web app that lets you run programming-language scripts, a task that would normally require special software and developer skills to carry out successfully. This process makes it easier to analyse the linguistic trends and themes of the content from a Search Engine Result Page.
‘N-gram co-occurrences’ is a script that allows us to count the most frequently occurring words and combinations in the SERPs, then analysing them and optimising our content using a more scientific approach to our target keywords.
Rory also explained how we can uncover content gaps within our landing pages and find new keywords that Google might see as semantically or contextually relevant to the keywords we’re already tracking and optimising for.
Additionally, a script called ‘Part of Speech’ allows us to dig more into those words and phrases based on their specific type (verbs, adjectives, nouns) making the analysis more accurate and detailed. For example, looking at the analysis that Rory did for the query ‘yoga’ we can see that ‘poses’ is the noun that appears more frequently in the SERPs’ content.
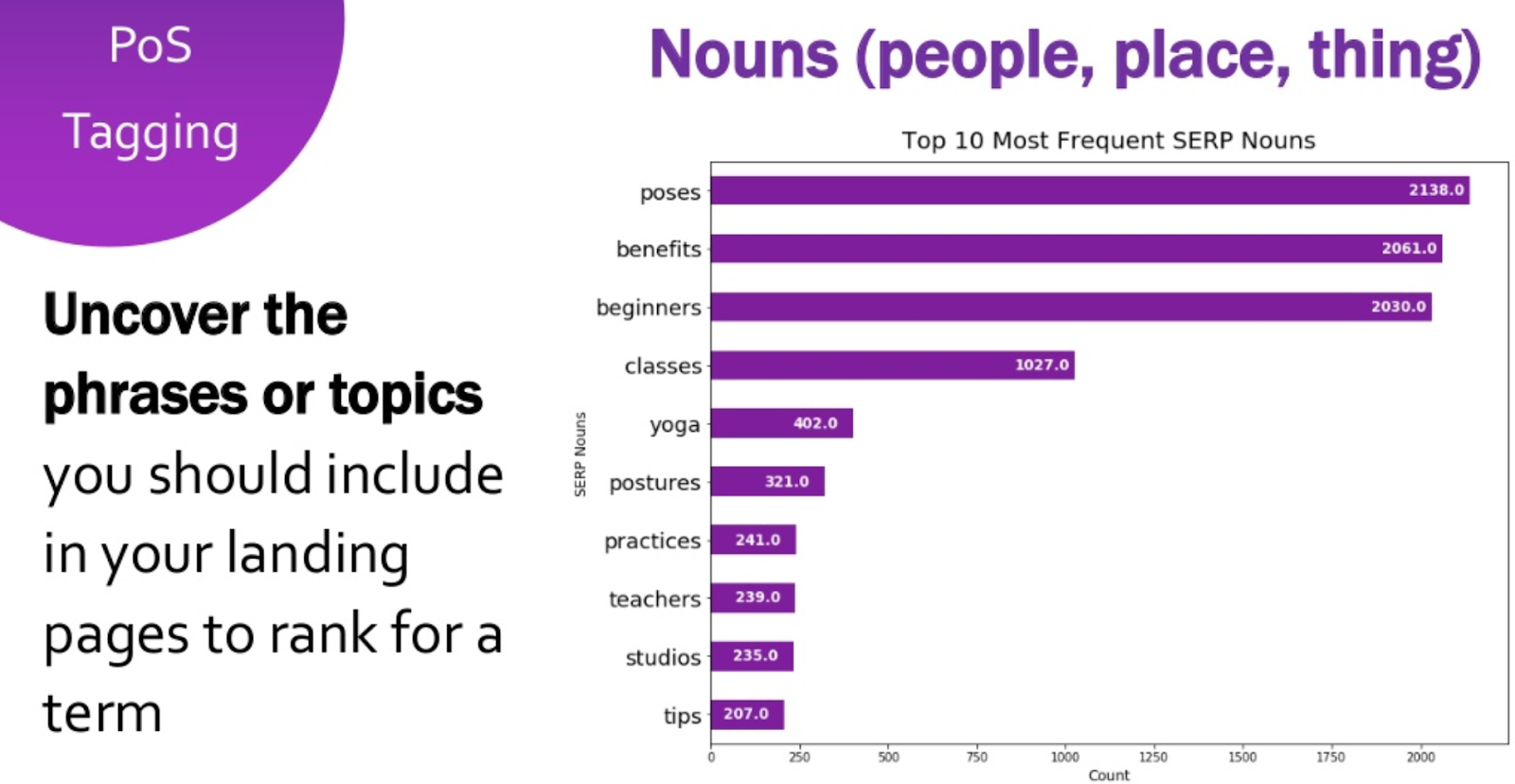
‘Topic Modeling’ is another script which allows us to determine topical trends within the SERPs and give us a glance at what Google identifies as topics of interest for the users. We can then use the analysis to build a content strategy across the website.
Key Takeaways:
- 84% of the SERPs meta description are algorithmically rewritten by Google
- Google will consciously pick content from the landing page that it thinks matches the search intent
- By using an open-source web application called Jupyter, we are able to scrape and analyse words, phrases and topics that Google thinks serve visitors better.
Charlie Norledge - What’s new in Structured Data
Charlie Norledge began the structured data session with his talk on what’s new in structured data.
In his talk, Charlie focused primarily on the latest Schema.org properties that produce rich results on Google. He spoke about winning SERP real-estate by using FAQ page schema and How-To schema markup. He also took a look at the niche-specific “Movie” schema which had just been announced days before BrightonSEO.
The reason that this Schema was interesting“Movie” schema was that some of the leading websites had already implemented this schema ahead of Google’s announcement of the rich results. Showing that it pays to implement all appropriately structured data markup to your site asap.
Charlie went on to give very practical advice on how we can find, create and implement the right schema for our own webpages. For example, by utilising Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool we can do a competitor analysis and take a look at what properties are being utilised by others as “inspiration”.
Overall, Charlie shared information that we currently provide to our SEO clients on structured data.
Key Takeaways:
- Always think about what’s coming next in Schema
- Be the first to implement new Schema
- Use structured data on AMP versions of your website
- Make sure to test structured data for both mobile and desktop
Lucinda Wood - Tips for optimising for Google Discover
Luci walked us through an upcoming vertical of search, ‘Google Discovery’ and gave some actionable insights and advice.

Google is using AI in order to serve users with content that might interest them and is more relevant to them based on interests and web interactions. Discovery is available for mobile devices and despite the fact that it’s a fairly new form, already boasts approx. 800 million monthly users, which is quite impressive.
Google Search Console allows us to monitor the performance of our pages in Discovery with a dedicated report within GSC. The performance report gives you visibility on clicks, impressions and click-through rates. Other metrics include:
- Total traffic generated from Discovery
- Best performing content
- How frequently your site appears in Discovery
- Split between traffic from Discovery and traditional search
It’s worth mentioning that this report will only show pages with meaningful visibility.
How to optimise for Google Discovery?
- Lucy recommends shifting your mindset from keywords to people
- Focus less on keywords and more on topics and audiences
- Learn what interests your audience and create appropriate content. Utilise YouGov profiler or affinity categories on Google Analytics
- Build fresh and evergreen content to maximise reach
- Look into the SERPs to get ideas from the featured snippets, People Also Ask or autosuggest
Key Takeaways:
- No need for structured data to appear on Google Discovery
- AMP Stories are hot right now, AMP is a big player in the latest Google informational /publishing verticals
- Focus on Audiences and relevancy, Journeys and values
- New and evergreen content is key
Eleni Cashell - How to turn a Press Release into unique ranking content
Eleni talked about Press Releases and walked us through the optimal steps to turn a boring piece of informative content into an asset that ranks in Search Engines and drives qualified traffic.
People want to hear from (and trust) other people and businesses. In fact, 642,000 press releases are being published each year. This means 1,759 press releases are being pushed out to the public every single day!
When considering a Press Release we should be making sure that we are creating relevant, high quality and unique content as this is the only way to turn the press releases into a valuable asset of our SEO campaigns.
We should be focusing on content that speaks to our audience and always think out of the box. Press releases don’t have to be just text style. The text could be converted to images, videos, etc.
Eleni advises us not to neglect category landing pages and put the brand/site news into a subfolder as this shows Google it's correctly structured. This will make the website more crawlable and more rapidly indexed.
Key Takeaways:
- Press releases don’t have to simply be in text form – Convert to images, video, etc. make them more exciting!
- Make sure to answer questions in order to obtain featured snippets
- Break up the content within the Press Release to make easier to crawl but having UX in mind
That’s all for now! Our clients will be getting a full BrightonSEO makeover on their websites over the coming months. Till next BrightonSEO, aloha!


.png)
.png)







_2025.png)

